备注
Go to the end to download the full example code.
计划¶
AgentScope 中的计划(Plan)模块使智能体能够正式地将复杂任务分解为可管理的子任务并系统地执行它们。主要功能包括:
支持 手动计划规范
- 全面的计划管理功能:
创建、修改、放弃和恢复 计划
在多个计划之间 切换
通过临时暂停计划来处理用户查询或紧急任务,优雅地处理中断
计划执行的 实时可视化和监控
备注
当前计划模块仅支持子任务按照顺序执行。
具体来说,计划模块的工作原理是
提供计划管理的工具函数
插入提示消息来指导ReAct智能体完成计划
下图说明了计划模块如何与ReAct智能体协作:
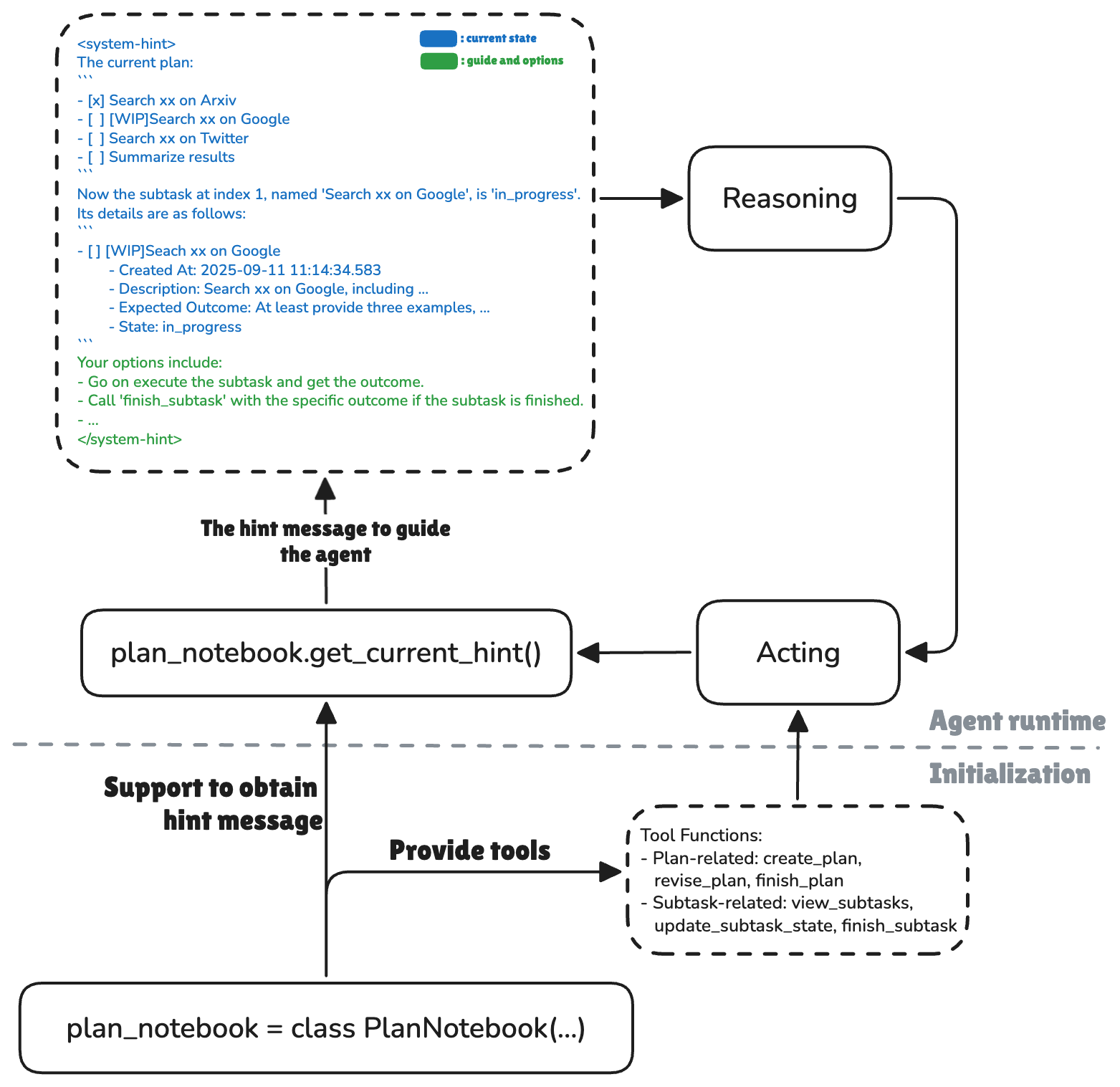
计划模块如何与ReAct智能体协作¶
import asyncio
import os
from agentscope.agent import ReActAgent
from agentscope.formatter import DashScopeChatFormatter
from agentscope.model import DashScopeChatModel
from agentscope.plan import PlanNotebook, Plan, SubTask
PlanNotebook¶
PlanNotebook 类是计划模块的核心,负责提供
管理计划,子任务的工具函数
提供用于“引导智能体正确完成任务”的提示消息(Hint message)
PlanNotebook 类使用以下参数实例化:
名称 |
类型 |
描述 |
|---|---|---|
|
|
计划中允许的子任务最大数量,如果为 |
|
|
基于当前计划的完成情况,生成对应提示消息的函数。如果未提供,将使用默认的 |
|
|
计划的存储模块,用于恢复,保存历史计划。如果未提供,将使用默认的内存(In-memory)存储。 |
plan_to_hint 参数是 PlanNotebook 类的核心参数,也是开发者进行提示工程的接口。
作为可调用对象,接受当前计划作为输入,并返回一个字符串类型的提示消息。
AgentScope 构建了一个默认的 DefaultPlanToHint 类,可以直接使用,同时我们鼓励开发者提供自己的 plan_to_hint 函数以获得更好的性能。
storage 用于存储历史计划,允许智能体检索和恢复历史计划。
我们同样鼓励开发者通过继承 PlanStorageBase 类来实现自己的计划存储。如果未提供,将使用默认的内存存储。
小技巧
PlanStorageBase 类继承自 StateModule 类,因此 storage也会通过会话管理进行保存和加载。
PlanNotebook 类的核心属性和方法总结如下:
类型 |
名称 |
描述 |
|---|---|---|
属性 |
|
智能体正在执行的当前计划 |
|
历史计划的存储,用于检索和恢复历史计划 |
|
|
一个可调用对象,以当前计划为输入并生成提示消息来指导智能体完成计划 |
|
函数 |
|
列出 |
|
获取当前计划的提示消息,将调用 |
|
create_plan,view_subtasks,revise_current_plan,update_subtask_state,finish_subtask,finish_plan,view_historical_plans,recover_historical_plan |
允许智能体管理计划和子任务的工具函数 |
|
|
注册一个钩子函数,当计划发生变化时将被调用,用于计划可视化和监控 |
|
|
移除已注册的钩子函数 |
list_tools 方法是获取所有工具函数的快速方法,这样您就可以将它们注册到智能体的工具包中。
plan_notebook = PlanNotebook()
async def list_tools() -> None:
"""列出PlanNotebook提供的工具函数。"""
print("PlanNotebook提供的工具:")
for tool in plan_notebook.list_tools():
print(tool.__name__)
asyncio.run(list_tools())
PlanNotebook提供的工具:
view_subtasks
update_subtask_state
finish_subtask
create_plan
revise_current_plan
finish_plan
view_historical_plans
recover_historical_plan
与ReActAgent协作¶
AgentScope中的 ReActAgent 已通过构造函数中的 plan_notebook 参数集成了计划模块。
一旦提供,智能体将
配备计划管理工具函数,并且
在每个推理步骤开始时插入提示消息
有两种方式在 ReActAgent 中使用计划模块:
开发者指定计划:开发者可以通过调用
create_plan工具函数手动创建计划,并使用该计划来初始化ReActAgent。智能体管理的计划执行:智能体将通过调用计划管理工具函数自己创建和管理计划。
手动计划规范¶
通过调用 create_plan 工具函数手动创建计划非常简单。
以下是手动创建计划以对LLM赋能的智能体进行全面研究的示例。
async def manual_plan_specification() -> None:
"""手动计划规范示例。"""
await plan_notebook.create_plan(
name="智能体研究",
description="对基于LLM的智能体进行全面研究",
expected_outcome="一份Markdown格式的报告,回答三个问题:1. 什么是智能体?2. 智能体的当前技术水平是什么?3. 智能体的未来趋势是什么?",
subtasks=[
SubTask(
name="搜索智能体相关调研论文",
description=(
"在多个来源搜索调研论文,包括"
"Google Scholar、arXiv和Semantic Scholar。必须"
"在2021年后发表且引用数超过50。"
),
expected_outcome="Markdown格式的论文列表",
),
SubTask(
name="阅读和总结论文",
description="阅读前一步找到的论文,并总结关键点,包括定义、分类、挑战和关键方向。",
expected_outcome="Markdown格式的关键点总结",
),
SubTask(
name="研究大公司的最新进展",
description=(
"研究大公司的最新进展,包括但不限于Google、Microsoft、OpenAI、"
"Anthropic、阿里巴巴和Meta。查找官方博客或新闻文章。"
),
expected_outcome="大公司的最新进展",
),
SubTask(
name="撰写报告",
description="基于前面的步骤撰写报告,并回答预期结果中的三个问题。",
expected_outcome=(
"一份Markdown格式的报告,回答三个问题:1. "
"什么是智能体?2. 智能体的当前技术水平"
"是什么?3. 智能体的未来趋势是什么?"
),
),
],
)
print("当前提示消息:\n")
msg = await plan_notebook.get_current_hint()
print(f"{msg.name}: {msg.content}")
asyncio.run(manual_plan_specification())
当前提示消息:
user: <system-hint>The current plan:
```
# 智能体研究
**Description**: 对基于LLM的智能体进行全面研究
**Expected Outcome**: 一份Markdown格式的报告,回答三个问题:1. 什么是智能体?2. 智能体的当前技术水平是什么?3. 智能体的未来趋势是什么?
**State**: todo
**Created At**: 2026-03-12 03:29:48.389
## Subtasks
- [ ] 搜索智能体相关调研论文
- [ ] 阅读和总结论文
- [ ] 研究大公司的最新进展
- [ ] 撰写报告
```
Your options include:
- Mark the first subtask as 'in_progress' by calling 'update_subtask_state' with subtask_idx=0 and state='in_progress', and start executing it.
- If the first subtask is not executable, analyze why and what you can do to advance the plan, e.g. ask user for more information, revise the plan by calling 'revise_current_plan'.
- If the user asks you to do something unrelated to the plan, prioritize the completion of user's query first, and then return to the plan afterward.
- If the user no longer wants to perform the current plan, confirm with the user and call the 'finish_plan' function.
</system-hint>
创建计划后,可以按如下方式使用计划笔记本初始化 ReActAgent :
agent = ReActAgent(
name="Friday",
sys_prompt="你是一个有用的助手。",
model=DashScopeChatModel(
model_name="qwen-max",
api_key=os.environ["DASHSCOPE_API_KEY"],
),
formatter=DashScopeChatFormatter(),
plan_notebook=plan_notebook,
)
智能体自主管理¶
智能体也可以通过调用计划管理工具函数自己创建和管理计划。
我们只需要按如下方式使用计划笔记本初始化 ReActAgent :
agent = ReActAgent(
name="Friday",
sys_prompt="你是一个有用的助手。",
model=DashScopeChatModel(
model_name="qwen-max",
api_key=os.environ["DASHSCOPE_API_KEY"],
),
formatter=DashScopeChatFormatter(),
plan_notebook=PlanNotebook(),
)
之后,我们可以构建一个循环来与智能体交互,如下所示。 一旦用户的任务复杂比较复杂,智能体将自己创建计划并逐步执行计划。
async def interact_with_agent() -> None:
"""与计划智能体交互。"""
user = UserAgent(name="user")
msg = None
while True:
msg = await user(msg)
if msg.get_text_content() == "exit":
break
msg = await agent(msg)
asyncio.run(interact_with_agent())
可视化和监控¶
AgentScope 通过钩子函数支持计划执行的实时可视化和监控。
当前计划被工具函数改变时,钩子函数将被触发,开发者可以在这些钩子函数中将当前的计划转发到对应的前端进行可视化或其他处理。 计划变化钩子函数的模板如下:
def plan_change_hook_template(self: PlanNotebook, plan: Plan) -> None:
"""计划变化钩子函数的模板。
Args:
self (`PlanNotebook`):
PlanNotebook实例。
plan (`Plan`):
当前计划实例(变化后)。
"""
# 将计划转发到前端进行可视化或其他处理
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.024 seconds)