Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Tools
Background
There are two ways to call tools in LLM-empowered multi-agent applications.
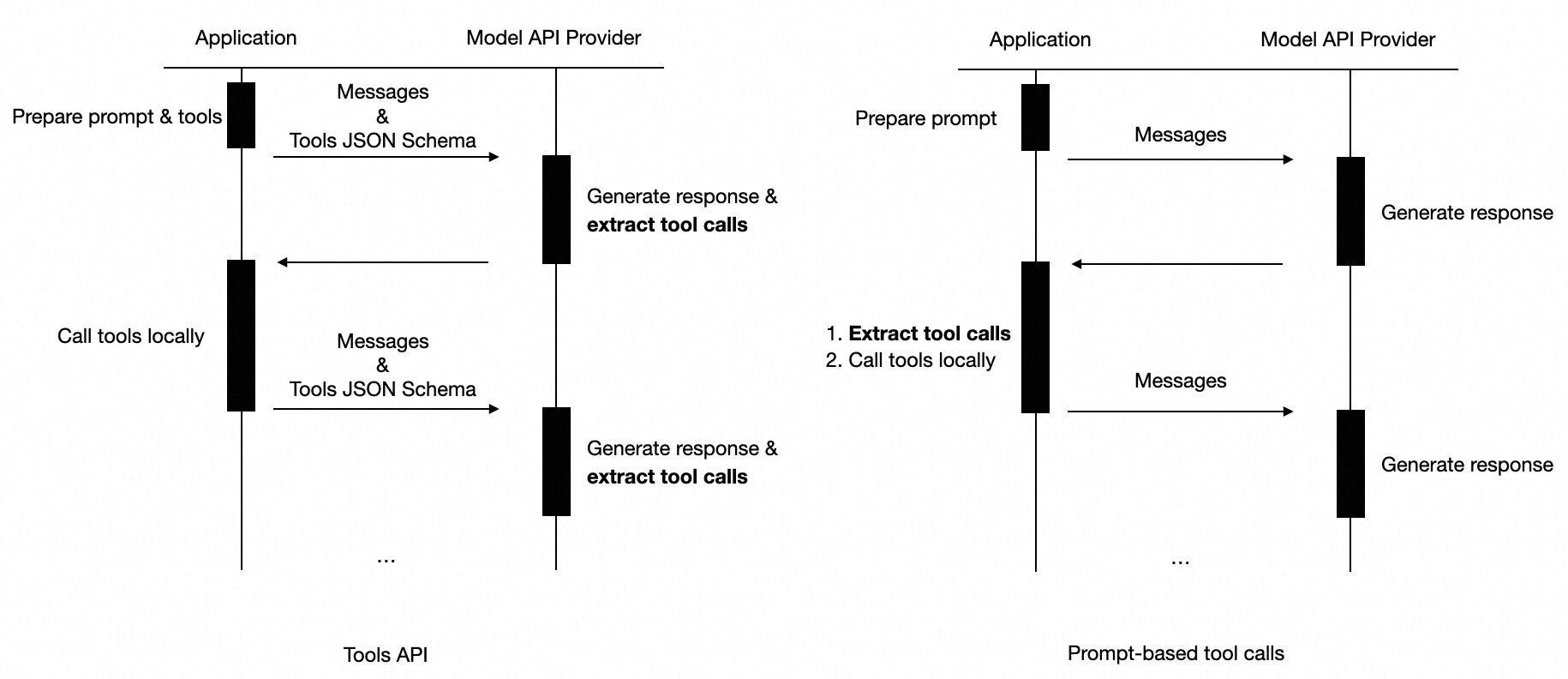
Prompt-based tool calling: Developers introduce tools in the prompt and extract tool calls from the LLM response.
API-based tool calling: Developers provide tools description in JSON schema format. The LLM API will directly return the tool calls in their specific format.
AgentScope supports both ways. In this tutorial, we will introduce how to use the built-in tools and how to create custom tools.
import json
import agentscope
from agentscope.message import Msg
from agentscope.models import DashScopeChatWrapper
Using Built-in Tools
AgentScope provides a ServiceToolkit module that supports to
parse tools into JSON schemas automatically
check arguments and call functions
Before using ServiceToolkit, we can take a look at the available tools in the agentscope.service module.
from agentscope.service import get_help, ServiceResponse, ServiceExecStatus
get_help()
All above functions are implemented as Python functions. They can be registered to the ServiceToolkit by calling the add method. The ServiceToolkit will parse the tool functions into JSON schema automatically.
from agentscope.service import ServiceToolkit
from agentscope.service import bing_search, execute_shell_command
toolkit = ServiceToolkit()
toolkit.add(execute_shell_command)
Note some parameters of the tool functions (e.g. api_key) should be handled by developers. You can directly pass these parameters as keyword arguments in the add method as follows, the reserved parameters will be left to the agent to fill.
toolkit.add(bing_search, api_key="xxx")
print("The tools instruction:")
print(toolkit.tools_instruction)
The tools instruction:
## Tool Functions:
The following tool functions are available in the format of
```
{index}. {function name}: {function description}
{argument1 name} ({argument type}): {argument description}
{argument2 name} ({argument type}): {argument description}
...
```
1. execute_shell_command: Execute given command and return the return code, standard output and
error within <returncode></returncode>, <stdout></stdout> and
<stderr></stderr> tags.
command (string): The shell command to execute.
timeout (number): The maximum time (in seconds) allowed for the command to run.
2. bing_search: Search question in Bing Search API and return the searching results
question (string): The search query string.
num_results (integer): The number of search results to return.
The built-in default calling format:
print(toolkit.tools_calling_format)
[{"name": "{function name}", "arguments": {"{argument1 name}": xxx, "{argument2 name}": xxx}}]
The JSON Schema description of the tool functions:
print(json.dumps(toolkit.json_schemas, indent=2))
{
"execute_shell_command": {
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "execute_shell_command",
"parameters": {
"properties": {
"command": {
"description": "The shell command to execute.",
"type": "string"
},
"timeout": {
"default": 300,
"description": "The maximum time (in seconds) allowed for the command to run.",
"type": "number"
}
},
"required": [
"command"
],
"type": "object"
},
"description": "Execute given command and return the return code, standard output and\n\nerror within <returncode></returncode>, <stdout></stdout> and\n<stderr></stderr> tags."
}
},
"bing_search": {
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "bing_search",
"parameters": {
"properties": {
"question": {
"description": "The search query string.",
"type": "string"
},
"num_results": {
"default": 10,
"description": "The number of search results to return.",
"type": "integer"
}
},
"required": [
"question"
],
"type": "object"
},
"description": "Search question in Bing Search API and return the searching results"
}
}
}
Prompt-based Tool Calling
In prompt-based tool calling, developers need to - introduce the tools and call format in prompt - parse and extract the tool calls from the LLM response.
You can use the parsers in Structured Output section to parse the LLM response and extract the tool calls. The tool call format of ServiceToolkit is as follows:
from agentscope.message import ToolUseBlock
tool_call = ToolUseBlock(
type="tool_use",
id="xxx",
name="bing_search",
input={"query": "AgentScope"},
)
After assembling the ServiceToolkit, you can integrate it into agent.
In AgentScope, we provide a ReActAgent to handle the tool usage, you can directly pass the ServiceToolkit object into this agent. Refer to builtin-agent for implementation details of this agent.
Note
ReActAgent constructs the prompt and parses the tools locally, rather than through the tools API provided by the model API. For using the tools API, please refer to tools-api.
from agentscope.agents import ReActAgent
agentscope.init(
model_configs={
"config_name": "my-qwen-max",
"model_type": "dashscope_chat",
"model_name": "qwen-max",
},
)
agent = ReActAgent(
name="Friday",
model_config_name="my-qwen-max",
service_toolkit=toolkit,
sys_prompt="You're a helpful assistant named Friday.",
)
msg_task = Msg(
"user",
"Help me to calculate 1615114134*4343434343",
"user",
)
res = agent(msg_task)
system: Respond with specific tags as outlined below:
<thought>{what you thought}</thought>
<function>{the function name you want to call}</function>
<{argument name}>{argument value}</{argument name}>
<{argument name}>{argument value}</{argument name}>
...
Friday: <thought>I need to calculate the multiplication of the two numbers provided by the user. I can use the execute_shell_command function to perform this calculation using a shell command.</thought>
<function>execute_shell_command</function>
<command>echo "1615114134*4343434343" | bc</command>
<timeout>60</timeout>
system: 1. Execute function execute_shell_command
[ARGUMENTS]:
{"command": "echo \"1615114134*4343434343\" | bc", "timeout": 60}
[RESULT]: <returncode>0</returncode>
<stdout>7015142197480303962
</stdout>
<stderr></stderr>
system: Respond with specific tags as outlined below:
<thought>{what you thought}</thought>
<function>{the function name you want to call}</function>
<{argument name}>{argument value}</{argument name}>
<{argument name}>{argument value}</{argument name}>
...
Friday: <thought>The multiplication of 1615114134 and 4343434343 has been calculated successfully, and the result is 7015142197480303962. I can now inform the user about this result.</thought>
<function>finish</function>
<response>The result of 1615114134 multiplied by 4343434343 is 7015142197480303962.</response>
system: 1. Execute function finish
[ARGUMENTS]:
{"response": "The result of 1615114134 multiplied by 4343434343 is 7015142197480303962."}
[RESULT]: The result of 1615114134 multiplied by 4343434343 is 7015142197480303962.
API-based Tool Calling
In API-based tool calling, developers only need to prepare the tools description in JSON schema format. However, different APIs differ in - the format of the tool description, and - how to construct the prompt with tool calls and execution results.

The above figure takes OpenAI as an example to show how API-based tool calling works in AgentScope. We block API-specific requirements by agentscope.formatter and ModelResponse modules. All developers need to know is
ServiceToolkit will parse the tool functions into standard JSON schema automatically
Formatter class will transform the JSON schemas and messages into the required format
The tool calls are all unified into the same format (ToolUseBlock) within ModelResponse
Tip
A new agent class ReActAgentV2 is added for API-based tools calling!
Note
Currently, only the format_chat method supports tools API. The format_multi_agent method will be supported in the future.
Note
API-based tool calling does not support streaming return yet, and the related functionality is under development.
Here we take DashScope as an example to show how to use the tools API.
from agentscope.formatters import DashScopeFormatter
from agentscope.message import TextBlock, ToolUseBlock, ToolResultBlock
model = DashScopeChatWrapper(
config_name="_",
model_name="qwen-max",
)
Step 3 -> 4 in the figure, formating messages and JSON schemas:
msgs = [
Msg("user", "Help me to execute shell cmd 'whoami'", "user"),
]
formatted_msgs = DashScopeFormatter.format_chat(msgs)
formatted_schemas = DashScopeFormatter.format_tools_json_schemas(
toolkit.json_schemas,
)
print(json.dumps(formatted_msgs, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False))
[
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"text": "Help me to execute shell cmd 'whoami'"
}
]
}
]
Step 5 -> 6 -> 7 in the figure, getting the model response:
response = model(formatted_msgs, tools=formatted_schemas)
print("tool_calls:", json.dumps(response.tool_calls, indent=4))
tool_calls: [
{
"type": "tool_use",
"id": "call_20370602ee234f92923d68",
"name": "execute_shell_command",
"input": {
"command": "whoami",
"timeout": 300
}
}
]
Step 8, creating a new message with the tool calls:
# Create a new msg with the tool calls
content = []
if response.text:
content.append(TextBlock(type="text", text=response.text))
if response.tool_calls:
content.extend(response.tool_calls)
msgs.append(Msg("assistant", content, "assistant", echo=True))
# execute the tool calls
msg_execution = toolkit.parse_and_call_func(
response.tool_calls,
tools_api_mode=True, # Must be ture for tools API
)
assistant: [
{
"type": "tool_use",
"id": "call_20370602ee234f92923d68",
"name": "execute_shell_command",
"input": {
"command": "whoami",
"timeout": 300
}
}
]
Step 9, adding the execution results to the message list:
msgs.append(msg_execution)
Now, let’s try to format the new message list with tool calls and result again!
formatted_msgs = DashScopeFormatter.format_chat(msgs)
print(json.dumps(formatted_msgs, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False))
[
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"text": "Help me to execute shell cmd 'whoami'"
}
]
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": null,
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "call_20370602ee234f92923d68",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "execute_shell_command",
"arguments": "{\"command\": \"whoami\", \"timeout\": 300}"
}
}
]
},
{
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": "call_20370602ee234f92923d68",
"content": "<returncode>0</returncode>\n<stdout>runner\n</stdout>\n<stderr></stderr>",
"name": "execute_shell_command"
}
]
Up to now, we have already finished the API-based tool calling process. The whole process refers to the implementation of agentscope.agents.ReActAgentV2 class. You can also directly use this agent.
Using MCP with ServiceToolkit
AgentScope provides support for integrating MCP (Model Context Protocol) servers, enabling enhanced capabilities for models and tools. You can add MCP servers to the ServiceToolkit using the add_mcp_servers method, where you specify the configurations for each server. Please note that MCP requires Python version >= 3.10.
configs = {
"mcpServers": {
"puppeteer": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-puppeteer"],
},
},
}
Add MCP server configurations to the ServiceToolkit toolkit.add_mcp_servers(server_configs=configs)
Creating Custom Tools
A custom tool function must follow these rules:
Typing for arguments
Well-written docstring in Google style
The return of the function must be wrapped by ServiceResponse
After calling the toolkit.add function, the tool function will be parsed automatically and registered to the ServiceToolkit.
def new_function(arg1: str, arg2: int) -> ServiceResponse:
"""A brief introduction of this function in one line.
Args:
arg1 (`str`):
Brief description of arg1
arg2 (`int`):
Brief description of arg2
"""
return ServiceResponse(
status=ServiceExecStatus.SUCCESS,
content="Done!",
)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 16.707 seconds)