Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Agent Hooks¶
Hooks are extension points in AgentScope that allow developers to customize agent behaviors at specific execution points, providing a flexible way to modify or extend the agent’s functionality without changing its core implementation.
In AgentScope, hooks are implemented around the agent’s core functions:
Agent Class |
Core Function |
Hook Types |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
AgentBase &its child classes
|
|
pre_replypost_reply |
The hooks before/after agent replying to a message |
|
pre_printpost_print |
The hook before/after printing a message to the target output (e.g., terminal, web interface) |
|
|
pre_observepost_observe |
The hooks before/after observing a message from the environment or other agents |
|
ReActAgentBase &its child classes
|
replyprintobserve |
pre_replypost_replypre_printpost_printpre_observepost_observe |
|
|
pre_reasoningpost_reasoning |
The hooks before/after the agent’s reasoning process |
|
|
pre_actingpost_acting |
The hooks before/after the agent’s acting process |
Tip
Since hooks in AgentScope are implemented using a metaclass, they support inheritance.
To simplify the usage, AgentScope provides unified signatures for all hooks.
import asyncio
from typing import Any, Type
from agentscope.agent import ReActAgentBase, AgentBase
from agentscope.message import Msg
Hook Signature¶
AgentScope provides unified hook signatures for all pre- and post-hooks as follows:
Pre-Hook Signature
Name |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
Arguments |
|
The agent instance |
|
The input arguments of the target
function, or the modified arguments
from the most recent non-None return
value of previous hooks
|
|
Returns |
|
The modified arguments or None |
Note
All positional arguments and keyword arguments of the core function are passed as a single kwargs dict to the hook functions
A pre-hook template is defined as follows:
def pre_hook_template(
self: AgentBase | ReActAgentBase,
kwargs: dict[str, Any],
) -> dict[str, Any] | None: # The modified displayed message
"""Pre hook template."""
pass
Post-Hook Signature
For post hooks, an additional output argument is added to the signature, which represents the output of the target function.
If the core function has no output, the output argument will be None.
Name |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
Arguments |
|
The agent instance |
|
A dict that contains all the arguments
of the target function
|
|
|
The output of the target function or
the most recent non-None return value
from previous hooks
|
|
Returns |
|
The modified arguments or None |
def post_hook_template(
self: AgentBase | ReActAgentBase,
kwargs: dict[str, Any],
output: Any, # The output of the target function
) -> Any: # The modified output
"""Post hook template."""
pass
Hook Management¶
AgentScope provides both instance- and class-level hooks, depending on the effective scope of the hooks. They execute in the following order:
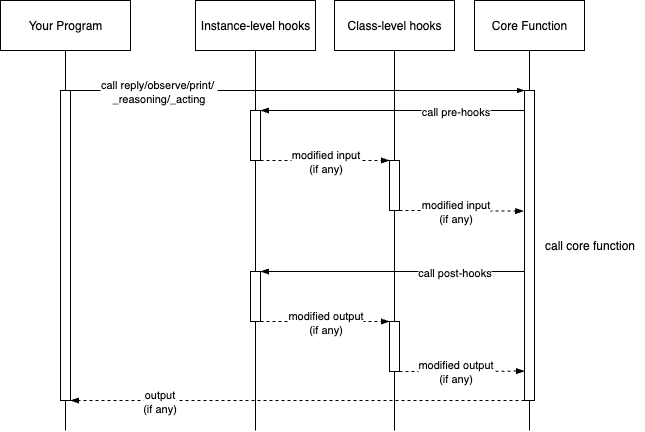
AgentScope provides built-in methods to manage hooks at both instance and class levels as follows:
Level |
Method |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Instance-level |
|
Register a hook for the current object with
given hook type and name.
|
|
Remove a hook for the current object with
given hook type and name.
|
|
|
Clear all hooks for the current object with
given hook type.
|
|
Class-level |
|
Register a hook for all objects of the class
with given hook type and name.
|
|
Remove a hook for all objects of the class
with given hook type and name.
|
|
|
Clear all hooks for all objects of the
class with given hook type.
|
When using hooks, you MUST follow these rules:
Important
Execution Order
Hooks are executed in registration order
Multiple hooks can be chained together
Return Value Handling
For pre-hooks: Non-None return values are passed to the next hook or core function
When a hook returns None, the next hook will use the most recent non-None return value from previous hooks
If all previous hooks return None, the next hook receives a copy of the original arguments
The final non-None return value (or original arguments if all hooks return None) is passed to the core function
For post-hooks: Works the same way as pre-hooks.
Important: Never call the core function (reply/speak/observe/_reasoning/_acting) within a hook to avoid infinite loops
Taking the following agent as an example, we can see how to register, remove and clear hooks:
# Create a simple test agent class
class TestAgent(AgentBase):
"""A test agent for demonstrating hooks."""
async def reply(self, msg: Msg) -> Msg:
"""Reply to the message."""
return msg
We create an instance-level hook and a class-level hook to modify the message content before replying.
# Create two pre-reply hooks
def instance_pre_reply_hook(
self: AgentBase,
kwargs: dict[str, Any],
) -> dict[str, Any]:
"""A pre-reply hook that modifies the message content."""
msg = kwargs["msg"]
msg.content += "[instance-pre-reply]"
# return modified kwargs
return {
**kwargs,
"msg": msg,
}
def cls_pre_reply_hook(
self: AgentBase,
kwargs: dict[str, Any],
) -> dict[str, Any]:
"""A pre-reply hook that modifies the message content."""
msg = kwargs["msg"]
msg.content += "[cls-pre-reply]"
# return modified kwargs
return {
**kwargs,
"msg": msg,
}
# Register class hook
TestAgent.register_class_hook(
hook_type="pre_reply",
hook_name="test_pre_reply",
hook=cls_pre_reply_hook,
)
# Register instance hook
agent = TestAgent()
agent.register_instance_hook(
hook_type="pre_reply",
hook_name="test_pre_reply",
hook=instance_pre_reply_hook,
)
async def example_test_hook() -> None:
"""An example function to test the hooks."""
msg = Msg(
name="user",
content="Hello, world!",
role="user",
)
res = await agent(msg)
print("Response content:", res.content)
TestAgent.clear_class_hooks()
asyncio.run(example_test_hook())
Response content: Hello, world![instance-pre-reply][cls-pre-reply]
We can see that a “[instance-pre-reply]” and a “[cls-pre-reply]” are added to the message content.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.002 seconds)