Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Tracing¶
AgentScope implements OpenTelemetry-based tracing to monitor and debug the execution of agent applications, which features
Provide built-in tracing for LLM, tool, agent, formatter, etc.
Support error and exception tracking
Provide native tracing visualization in AgentScope Studio
Support connecting to third-party platforms like Alibaba Cloud CloudMonitor, Arize-Phoenix, Langfuse, etc.
Setting Up¶
Note
Connecting to the AgentScope Studio or third-party tracing endpoint should be done at the beginning of your application by the agentscope.init function.
AgentScope Studio¶
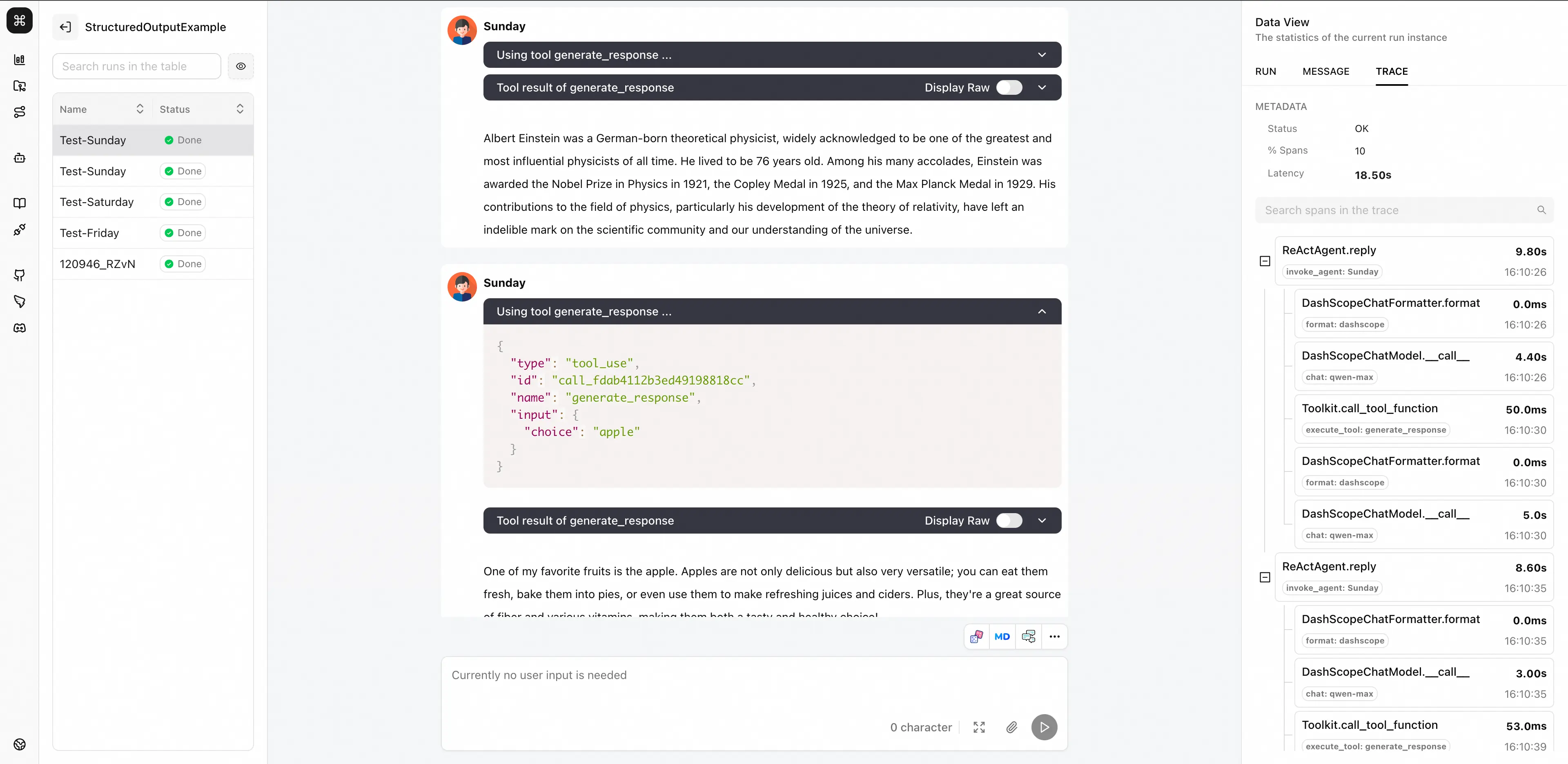
Tracing in AgentScope Studio¶
When connecting to AgentScope Studio, just provide studio_url parameter in agentscope.init function.
import agentscope
agentscope.init(studio_url="http://xxx:port")
Third-party Platforms¶
To connect to third-party tracing platforms, set the tracing_url parameter in the agentscope.init function.
The tracing_url is the URL of your OpenTelemetry collector or any compatible backend that supports OTLP (OpenTelemetry Protocol).
import agentscope
# Connect to OpenTelemetry-compatible backends
agentscope.init(tracing_url="https://your-tracing-backend:port/traces")
Taking Alibaba Cloud CloudMonitor, Arize-Phoenix, and Langfuse as examples:
Alibaba Cloud CloudMonitor: A fully-managed observability platform.
agentscope.init(tracing_url="https://tracing-cn-hangzhou.arms.aliyuncs.com/adapt_xxx/api/otlp/traces")
Tip
Get your Endpoint: In the ARMS Console under Access Center > OpenTelemetry,
select the Public Endpoint matching your deployment region. Customize your app name via the OTEL_SERVICE_NAME environment variable.
Alibaba Cloud CloudMonitor provides zero-code instrumentation through LoongSuite agent.
Learn more in the CloudMonitor Documentation.
Arize-Phoenix: You need to set the PHOENIX_API_KEY in your environment variables.
# Arize Phoenix Integration
import os
PHOENIX_API_KEY = os.environ.get("PHOENIX_API_KEY")
os.environ["OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS"] = f"api_key={PHOENIX_API_KEY}"
agentscope.init(tracing_url="https://app.phoenix.arize.com/v1/traces")
LangFuse: You need to set the LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY and
LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY in your environment variables. The authorization
header is constructed using these keys.
import os, base64
LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY = os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"]
LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY = os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"]
LANGFUSE_AUTH_STRING = f"{LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY}:{LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY}"
LANGFUSE_AUTH = base64.b64encode(LANGFUSE_AUTH_STRING.encode("utf-8")).decode("ascii")
os.environ["OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS"] = f"Authorization=Basic {LANGFUSE_AUTH}"
# EU data region
agentscope.init(tracing_url="https://cloud.langfuse.com/api/public/otel/v1/traces")
# US data region
# agentscope.init(tracing_url="https://us.cloud.langfuse.com/api/public/otel/v1/traces")
Customizing Tracing¶
As stated above, the tracing in AgentScope is implemented based on OpenTelemetry. That means your own tracing code implemented by OpenTelemetry sdk is compatible with AgentScope natively.
Besides, AgentScope has built-in the following decorators to trace the corresponding modules:
@trace_llm: Trace the__call__function of classes inherit fromChatModelBase@trace_reply: Trace thereplyfunction of classes inherit fromAgentBase@trace_format: Trace theformatfunction of classes inherit fromFormatterBase@trace: Trace general functions
Tracing LLMs¶
The @trace_llm decorator is to trace the __call__ function of ChatModelBase classes.
Note
Your LLM class must inherit from ChatModelBase
class ExampleChatModel(ChatModelBase):
"""An example Model"""
...
@trace_llm
async def __call__(
self,
*args: Any,
**kwargs: Any,
) -> AsyncGenerator[ChatResponse, None] | ChatResponse:
"""LLM call"""
...
Tracing Agent¶
The @trace_reply decorator is for agent implementations and tracing the reply function.
Note
Your agent class must inherit from AgentBase
class ExampleAgent(AgentBase):
"""An example agent class"""
@tracer_reply
async def reply(self, *args: Any, **kwargs: Any) -> Msg:
"""Reply to the message."""
...
Tracing Formatter¶
The @trace_format decorator is for formatters implementations and tracing the format function.
Note
Your formatter class must inherit from FormatterBase
class ExampleFormatter(FormatterBase):
"""A simple example formatter class"""
@trace_format
async def format(self, *args: Any, **kwargs: Any) -> list[dict]:
"""Example formatting"""
General Tracing¶
The @trace decorator is different from the above decorators, as it is a general-purpose tracing decorator that can be applied to any function.
It requires a name parameter to identify the traced function, and can trace various types of functions, including:
synchronous functions
synchronous generator functions
asynchronous functions
asynchronous generator functions
# 1. Synchronous function
@trace(name='simple_function')
def simple_function(name: str, age: int) -> str:
"""A simple function with automatic tracing."""
return f"Hello, {name}! You are {age} years old."
# 2. Synchronous generator function
@trace(name='number_generator')
def number_generator(n: int) -> Generator[int, None, None]:
"""Generate numbers from 0 to n-1."""
for i in range(n):
yield i
# 3. Asynchronous function
@trace(name='async_function')
async def async_function(data: dict) -> dict:
"""Process data asynchronously."""
return {"processed": data}
# 4. Asynchronous generator function
@trace(name='async_stream')
async def async_stream(n: int) -> AsyncGenerator[str, None]:
"""Generate stream of data asynchronously."""
for i in range(n):
yield f"data_{i}"
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.000 seconds)